Ultrasound and genetic testing can detect over 80 percent of all malformations prior to birth. However, there is no such thing as a medical guarantee for a completely healthy child.
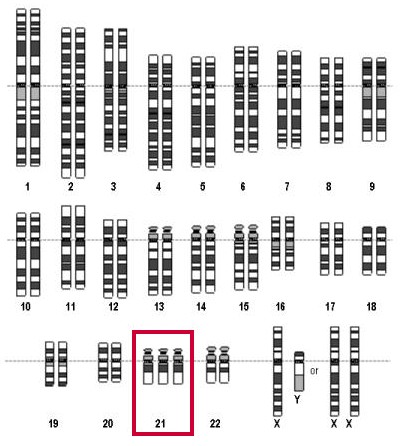
Prenatal testing in the narrower sense checks the genetic code of the unborn baby. The most common problem is the so-called Down's syndrome (trisomy 21), where the baby carries three instead of two copies of chromosome number 21 (marked in red). The frequency of trisomy 21 heavily depends on the age of the mother (see table of risk figures in chapter 4.5).
Nuchal translucency (NT)
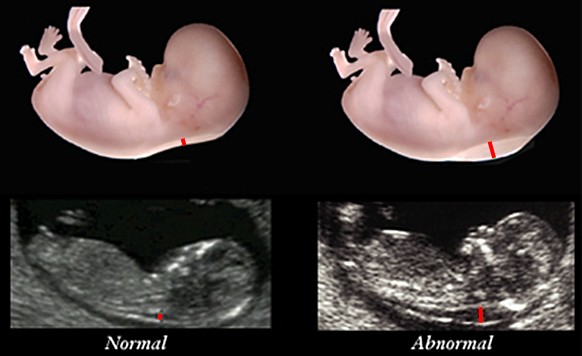
This relatively new warning sign for a genetic problem is being checked by ultrasound between week 11 and 14. The fetus should have a minimal crown-rump-length of 38 millimeters to give a meaningful reading. The examination requires experience, a good ultrasound device and maximum magnification. At this stage of development, it is normal for a fetus to have a thin layer of liquid in the nuchal region (small red line on bottom left); nuchal translucencies superior to 3.5 millimeters (bottom right), however, document a problem of lymphatic drainage and are highly suspicious of a genetic problem and/or malformations.
How to proceed if the NT is superior to 2.5 mm (5% of all pregnant women)
In case of abnormal NT findings, invasive prenatal testing by chorionic biopsy or amniocentesis is recommended (see chapter 4.4). A NT of 2.5 - 3.4 mm corresponds to a gray zone, whereas NTs of 3.5 mm and more (which occur in 1% of pregnancies) should be investigated further on all accounts.
First trimester blood test
Your individual risk of trisomy 21 as well as trisomy 18/13 can be calculated statistically by providing the age of the mother, the nuchal translucency and a blood sample. This test is a statistical estimate, not a definite diagnosis. The first trimester blood test is covered by health insurance and is available within a few days.
Measuring NT alone detects approx. 70% of fetuses with trisomy 21 (Down's syndrome); the combination with the first trimester blood test detects between 80% and 90%.